The transportation sector is currently a relatively mature field for hydrogen energy applications, with demonstrative applications realized in hydrogen-powered buses, heavy trucks, ships, airplanes, and forklifts. As hydrogen energy continues to develop in the transportation sector, hydrogen refueling stations, as crucial infrastructure for hydrogen transportation, have attracted high attention from the government to industry chain enterprises. According to the data from the "China Hydrogen Refueling Station Construction and Operation Industry Development White Paper (2023)," by the first half of 2023, a total of 1,089 hydrogen refueling stations have been built globally, of which 351 have been constructed in China, accounting for 32.2% of the global total. With strong guidance and support from national and local policies, it is expected that there will be over 1,000 stations by 2025.
1.1 Hydrogen energy, due to its light weight, abundant reserves, and good combustion performance, is considered a new type of energy for China's low-carbon energy transition and is also seen as an important way to achieve carbon neutrality across various industries. The transportation sector is currently a relatively mature field for hydrogen energy applications, with demonstrative applications realized in hydrogen-powered buses, heavy trucks, ships, airplanes, and forklifts.
1.2 With the continuous development of hydrogen energy in the transportation sector, hydrogen refueling stations, as vital infrastructure for hydrogen transportation, have garnered significant attention from governments to industry enterprises. According to the "China Hydrogen Refueling Station Construction and Operation Industry Development White Paper (2023)," by the first half of 2023, a total of 1,089 hydrogen refueling stations have been built worldwide, with 351 of those in China, accounting for 32.2% of the global total. Under the strong guidance and support of national and local policies, it is anticipated that the number will exceed 1,000 stations by 2025.
1.3 Currently, 99% of the hydrogen refueling stations built in China adopt an external hydrogen supply model, primarily using 20MPa tube containers carried by long-tube trailers for hydrogen transportation. The external hydrogen supply method has low transportation capacity (the mass of hydrogen carried is about 1% of the total mass of the trailer), long loading and unloading times (generally requiring about 4 hours), high transportation costs, and low overall energy efficiency. As a result, the storage and transportation costs of hydrogen account for 20%-30% of the actual end-terminal hydrogen costs. It is evident that the storage and transportation of hydrogen are critical factors affecting the market competitiveness of hydrogen energy.
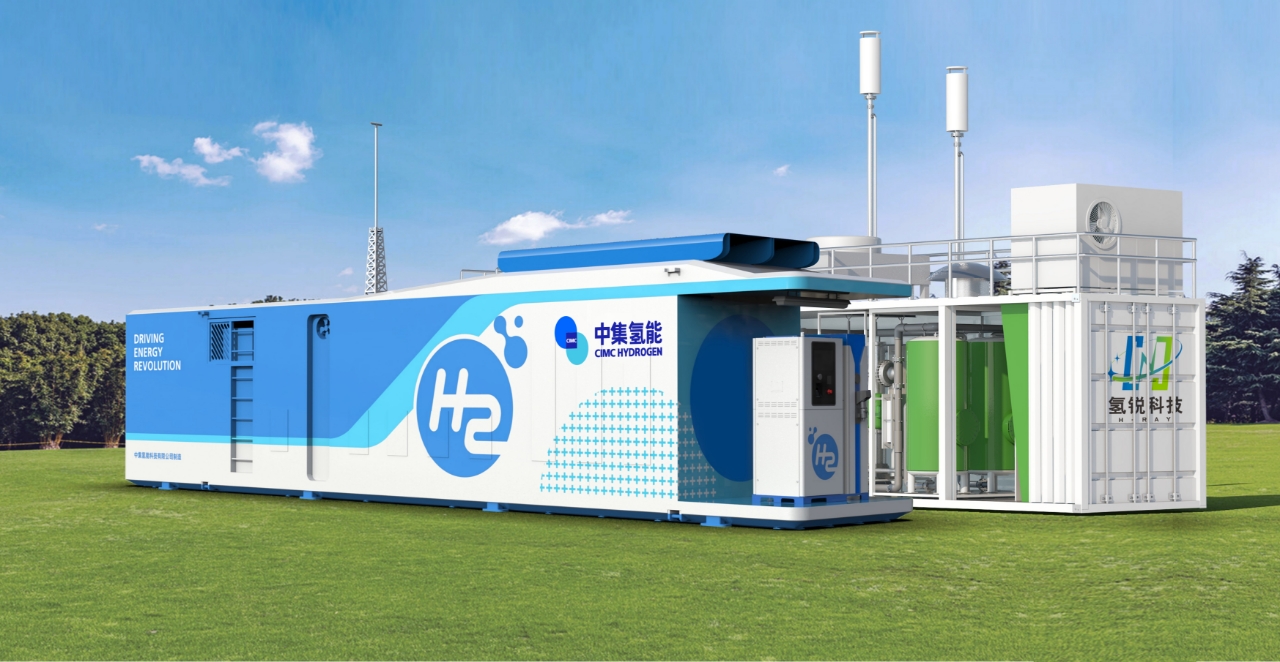
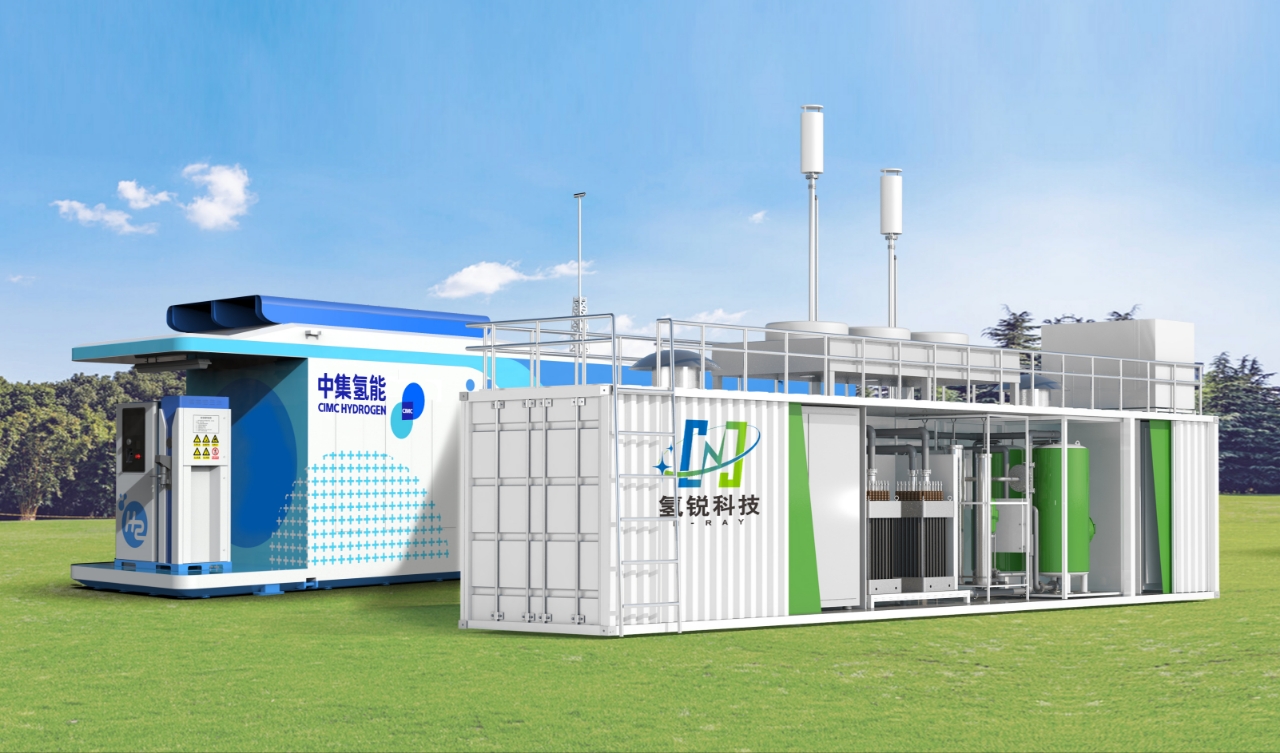
1.4 If a model of an integrated hydrogen production and refueling station can be implemented within the site, it would reduce the intermediate storage and transportation links and eliminate the costly hydrogen transportation expenses, effectively addressing the issue of high costs associated with hydrogen storage and transportation.
1.5 As national policies gradually relax control over the construction of integrated stations, many provinces and regions across the country have introduced relevant policies to encourage the integrated construction of hydrogen production and refueling. More and more areas are allowing hydrogen production outside of chemical industrial parks and easing document management. The policies imply that the constraints on the development of the hydrogen energy industry are gradually loosening, which will have a positive effect on the development of integrated hydrogen production and refueling stations, giving the hydrogen energy industry more "breathing space."
1.6 Guangdong Province is the first to take the initiative and is also a highland for the development of hydrogen energy. The Guangdong Provincial Government's "Interim Measures for the Management of Hydrogen Refueling Stations for Fuel Cell Vehicles in Guangdong Province (Draft for Comments)" (hereinafter referred to as the "Measures") explicitly proposes to allow the construction of integrated hydrogen production and refueling stations outside chemical industrial parks. The industry believes that this policy will have a positive impact on the hydrogen energy industry, and the construction of integrated hydrogen production and refueling stations outside chemical industrial parks in Guangdong is expected to be "loosened." Subsequently, Zhejiang Province also made corresponding revisions. The "Zhejiang Province Safety Production Regulations (Revised in 2022)" are expected to further promote the development of integrated hydrogen production and refueling stations beyond chemical industrial parks, benefiting industry development. Sichuan Province, Shandong Province, Shanghai City, Wuhan City in Hubei Province, and Tangshan City in Hebei Province have all followed suit.
1.7 At the beginning of 2023, Dalian introduced the first technical specification for integrated stations in the country, "Technical Specification for Hydrogen Production and Refueling Integrated Stations in the Dalian Area (Bonded Zone) of China (Liaoning) Pilot Free Trade Zone." Subsequently, Guangdong Province also issued an announcement on the local standard opinions for the "Safety Technical Specification for Integrated Stations (Draft for Approval)." There have been breakthroughs both in the standards for hydrogen production and refueling integration and in their actual implementation. News of the construction of integrated stations across the country is beginning to increase.